Tryptamines
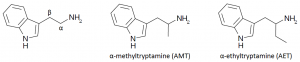
Alpha Substituted Tryptamines
The tryptamine backbone provides a building block for a large number of research chemicals. One such class is the alpha-substituted tryptamines. There are two carbons between the amine group (NH2) and the indole ring of tryptamine, referred to as alpha and beta. Short alkyl chains have successfully been substituted at the alpha position nearest the amine group.
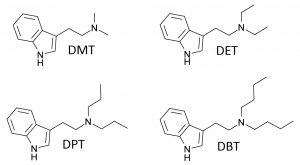
N-Alkylated Tryptamines
The amine group of tryptamine possesses a nitrogen with two hydrogens where functional groups can be substituted. The simple case where both of these substitutions are identical includes the best known example dimethyltryptamine (DMT). We can also consider asymmetrical cases where the two substitutions are different.
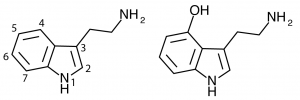
4-Hydroxy Tryptamines
The indole ring of tryptamine provides a number of possible locations for functional groups to be substituted. Addition of a hydroxy group at the 4-position produces a large number of psychedelic compounds including some true classics.
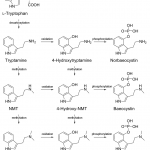
Grid Biosynthesis of Psilocybin
The biosynthesis of psilocybin in psychedelic mushrooms is a multi-step process, and the precise mechanism is debated by many authors. The essential amino acid l-tryptophan undergoes several modifying reactions but the specific order is unclear. A specific series of steps is generally accepted, but an elegant alternative incorporating multiple paths to psilocybin has been proposed.
Biosynthesis of 4-Substituted Tryptamine Derivatives
Biological organisms are wondrous little molecular factories, their enzyme catalyzed reactions often accomplishing in a single step what would confound a chemist in a well-stocked laboratory. Researchers have attempted to harness these biosynthetic pathways to create complex molecules not easily synthesized by conventional methods.


No comments yet.